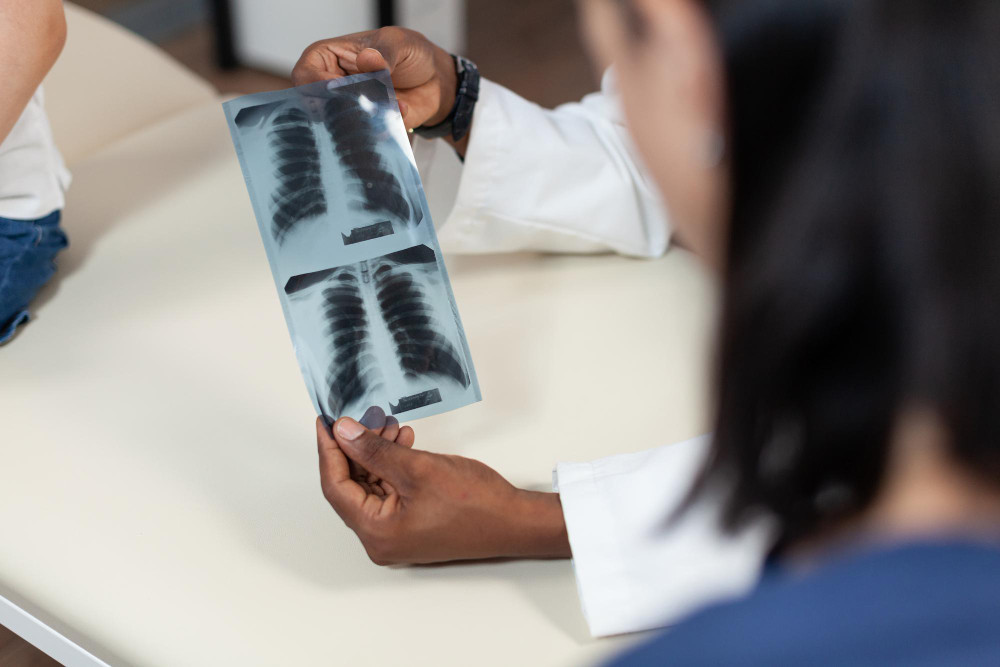
Penyakit tuberkulosis atau yang dikenal dengan istilah TB adalah penyakit infeksi yang disebabkan oleh bakteri Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Penyakit ini utamanya menyerang paru-paru namun juga dapat menyerang organ lainnya seperti saraf, tulang, dan kelenjar.
Penularan tuberkulosis terjadi ketika seseorang menghirup udara yang terkontaminasi bakteri TB melalui bersin atau percikan air liur. Namun, tidak semua orang yang terinfeksi bakteri TB akan muncul gejala TB. Kondisi ini dikenal dengan istilah TB laten dimana virus TB tidak aktif.
Perbedaan Antara TB Laten dan TB Aktif
Berbeda dengan penyakit infeksi bakteri lainnya, orang yang terinfeksi bakteri TB umumnya tidak segera menunjukkan gejala. Dilansir dari Everyday Health, TB umumnya dibagi menjadi tiga tahapan, yaitu:
- Infeksi primer, yaitu terjadi saat menghirup udara yang mengandung bakteri TBC. bakteri masuk melalui rongga mulut dan hidung lalu tiba di paru-paru dan memperbanyak diri.
- Infeksi TB laten, terjadi saat sistem kekebalan tubuh mampu menahan perkembangan infeksi bakteri sehingga bakteri TB bersifat dorman atau tidak aktif.
- Infeksi TB aktif, terjadi ketika sistem kekebalan tubuh melemah dan bakteri yang sebelumnya dorman akhirnya bangkit dan mulai menginfeksi.
Seringkali orang tidak menyadari bahwa mereka sedang berada di tahap TB laten karena TB laten tidak menunjukkan gejala yang khas.
Dilansir dari CDC, ada perbedaan mendasar antara TB laten dan TB aktif, di antaranya:
1. TB Laten
Pada tahapan ini, seseorang dapat dikatakan sudah terinfeksi TB namun tidak menunjukkan gejala apa pun. Karakteristik TB laten antara lain:
- Tidak merasa sakit
- Tidak dapat menularkan bakteri TB pada orang lain
- Pemeriksaan TB menunjukkan hasil positif, rontgen dada normal dan tes sputum menunjukkan hasil negatif
Orang yang memiliki TB laten tidak selalu berkembang menjadi TB aktif. Jika memiliki daya tahan tubuh yang baik, bakteri TB dapat bertahan dalam status dorman untuk jangka waktu yang cukup lama. Begitu juga sebaliknya, jika daya tahan tubuh lemah maka bakteri TB dengan mudah akan aktif, berkembang biak dan menyebabkan TB aktif.
2. TB Aktif
TB aktif merupakan tahapan lanjutan dari TB laten apabila daya tahan tubuh tidak mampu menahan perkembangan bakteri TB dalam tubuh. Tahapan TB aktif ini ditandai dengan beberapa hal berikut:
- Pasien TB menunjukkan gejala seperti demam, batuk berdahak, berat badan turun
- Pasien TB dapat menularkan bakteri TB pada orang lain
- Hasil rontgen dada menunjukkan pembercakan paru dan hasil tes sputum positif
Apabila dokter telah menetapkan Anda mengalami diagnosis TB aktif, maka dokter kemudian akan merekomendasikan pengobatan yang tepat sesuai hasil pemeriksaan.
Anda dapat membaca juga artikel mengenai TB berikut ini:
Apa Saja Gejala Tuberkulosis (TB) yang Perlu Diwaspadai?
Bagaimana Mendiagnosis TB Laten?
Kondisi TB laten seringkali tidak diketahui melalui pemeriksaan fisik karena umumnya tidak menunjukkan gejala. Untuk mengetahuinya, seseorang perlu melakukan tes Mantoux, yaitu tes yang dilakukan dengan menyuntikkan tuberkulin ke kulit di bawah lengan. Selain tes Mantoux, dokter juga akan meminta pasien melakukan pemeriksaan lain seperti rontgen dada dan tes dahak.
Bagi Anda yang berisiko tinggi mengalami TB laten seperti orang yang memiliki sistem kekebalan lemah dan berinteraksi dengan pengidap TB dan tenaga kesehatan yang merawat pasien TB maka sebaiknya melakukan pemeriksaan TB jika mengalami kontak erat.
Pengobatan TB Laten
Meskipun pengidap TB laten tidak dapat menularkan bakteri TB ke orang lain, namun TB laten perlu mendapat pengobatan agar tidak berkembang menjadi TB aktif. Beberapa pengobatan untuk mengatasi TB laten antara lain isoniazid, rifapentine dan rifampin. Pengobatan TB laten dapat memakan waktu 4-9 bulan tergantung pada kondisi TB laten yang dialami.
Penyakit tuberkulosis merupakan salah satu penyakit infeksi yang mematikan di berbagai belahan dunia termasuk Indonesia. Dengan pemeriksaan dan pencegahan yang tepat, Anda dapat terhindar dari infeksi tuberkulosis. Segera periksakan ke dokter apabila Anda kontak erat dengan pasien TB dan menunjukkan gejala batuk yang tak kunjung sembuh.
Baca selengkapnya mengenai penyakit tuberkulosis (TB) di sini. Anda juga bisa temukan lebih banyak artikel mengenai penyakit pada laman ini, ya!
- dr Ayu Munawaroh, MKK
CDC. (2020). Latent TB Infection and TB Disease. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/tb/topic/basics/tbinfectiondisease.htm
CDC. (2021). Questions and Answers About Tuberculosis. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/tb/publications/faqs/tb-qa.htm
CDC. (2020). Treatment Regimens for Latent TB Infection (LTBI). Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/tb/topic/treatment/ltbi.htm
Goldman, R. (2018). Latent Tuberculosis Infection vs. Active TB Disease: What’s the Difference?. Available from: https://www.everydayhealth.com/tuberculosis/guide/latent/#