Brand/Nama Lain
Acetazolamid, Glauseta, Cenda Glaucon
Cara Kerja
Acetazolamide merupakan obat yang memiliki manfaat untuk menurunkan tekanan di dalam bola mata. Selain itu, obat ini juga berfungsi sebagai diuresis yang bekerja dengan membuang air yang berlebih di dalam tubuh, dan menghambat enzim yang bernama karbonik anhidrase.
Indikasi
Obat ini digunakan pada kondisi medis berupa:
- Glaucoma
- Kondisi untuk diuresis atau pengeluaran cairan berlebih apabila ada edema (pembengkakan akibat penimbunan cairan di dalam organ)
- Gagal jantung kongestif
- Pencegahan Altitude sickness atau penyakit pada ketinggian
- Tekanan darah tinggi dalam kepala
- Epilepsi
Kontraindikasi
Acetazolamide tidak boleh digunakan bila seseorang memiliki kondisi medis seperti:
- Riwayat hipersensitivitas atau alergi terhadap senyawa sulfonamid (misalnya biduran atau bengkak pada kelopak mata)
- Asidosis hiperkloremia, kondisi ketika pH darah <7,35 atau asam karena peningkatan ion klorida di darah
- Sirosis liver atau pengerasan hati
- Gangguan liver berat
- Gagal ginjal berat
Efek Samping
Efek samping umumnya jarang terjadi. Meskipun demikian, ada beberapa efek samping yang mungkin terjadi, misalnya:
- Gangguan keseimbangan elektrolit tubuh seperti kekurangan kalium (hipokalemia) atau natrium (hiponatremia)
- Rasa mendengung pada telinga
- Mual
- Muntah
- Diare
- Kelelahan
- Sakit kepala
- Hilang nafsu makan
- Reaksi pada kulit seperti muncul bercak merah atau biduran
Sediaan
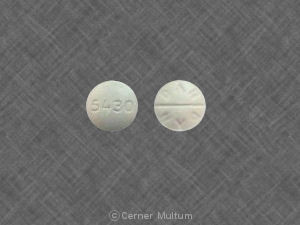
Sediaan acetazolamide yang dapat ditemukan hingga saat ini adalah sebagai tablet 250 mg.
Dosis
Tujuan: sebagai diuresis
Dosis dewasa: 250 -375 mg sekali sehari
Tujuan: untuk mengobati glaukoma atau persiapan sebelum operasi glaukoma
Dosis dewasa: 250 – 1000 mg sekali sehari dapat diberikan dalam dosis terbagi dalam sehari.
Tujuan: untuk mengobati altitude sickness
Dosis dewasa: 250 - 500 mg sehari, dalam dua dosis terbagi
Keamanan
Kehamilan:
Termasuk FDA kategori C (terdapat penelitian pada hewan uji coba yang menunjukkan adanya efek samping pada janin namun tidak ada penelitian terkontrol baik dan memadai pada manusia) sehingga potensi manfaat dan risiko obat perlu dipertimbangkan dan digunakan dengan hati-hati pada ibu hamil.
Interaksi Obat
Obat-obatan antikejang (fenitoin atau karbamazepin)
Penggunaan obat secara bersamaan antara acetazolamide dan obat-obatan antikejang seperti fenitoin atau karbamazepine memiliki potensi interaksi obat. Dapat terjadi peningkatan kadar obat antikejang tersebut di dalam tubuh sehingga risiko timbulnya efek samping obat antikejang jadi semakin meningkat.
Mau tahu informasi seputar obat-obatan lainnya? Cek di sini, ya!
- dr Hanifa Rahma
Badan Pengawas Obat dan Makanan. Asetazolamid. Available from: https://pionas.pom.go.id/monografi/asetazolamid
Mims Indonesia. Acetazolamide. Available from: https://www.mims.com/indonesia/drug/info/acetazolamide?mtype=generic
Badan Pengawas Obat dan Makanan. Acetazolamide. Available from: https://cekbpom.pom.go.id//home/produk/8lba1fsrc3h2gb9uv6hob4ek60/all/row/10/page/1/order/4/DESC/search/5/acetazolamide
Farzam, K., Abdullah, M. (2021). Acetazolamide. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532282/