Definition
Polydactyly is a condition in which a baby is born with extra fingers or toes. The term comes from the Greek words poly (many) and dactylos (finger). It is a common congenital abnormality, where the extra digits can appear on one or both hands or feet. Polydactyly often runs in families.
Polydactyly Variations
Polydactyly can present in different forms, including:
-
Nubbins: Small lumps of soft tissue without bones.
-
Partial formation of a finger or thumb: These have bone but lack joints.
-
Fully functional fingers or thumbs: These are complete with tissue, bone, and joints.
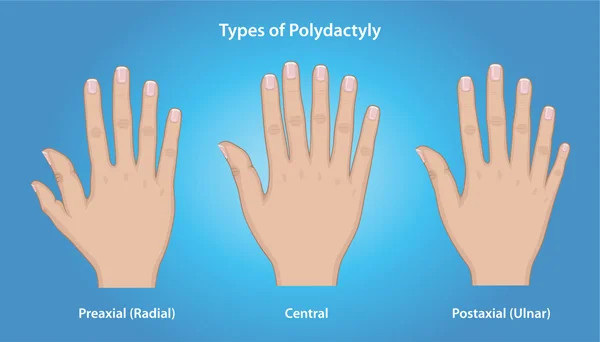
Types of Polydactyly
Based on the appearance of the duplicated fingers or toes, polydactyly is classified into three main types:
- Duplication of the little finger (ulnar or postaxial polydactyly)
-
This is the most common type, where the extra finger is on the little finger (on the ulnar side of the hand). When this type affects the big toe, it is referred to as fibular polydactyly.
-
- Duplication of the thumb (radial or preaxial polydactyly)
-
This is a less common condition, occurring in 1 in 1,000 to 10,000 births. The extra finger appears on the outside of the thumb (on the radial side). When this type affects the big toe, it is called tibial polydactyly.
-
- Middle or central polydactyly
-
A rare form, where the extra digit appears on the middle, ring, or, most commonly, the index finger.
-
Causes
Polydactyly is primarily caused by genetic factors and can be inherited. When the condition is passed down through families, it is called familial polydactyly. In some cases, polydactyly can be associated with genetic syndromes. Conditions that may be linked to polydactyly include:
-
Syndactyly: A condition where two or more toes are fused together.
-
Jeune Syndrome (Asphyxiating Thoracic Dystrophy)
-
Down Syndrome
-
Carpenter Syndrome
-
Ellis van Creveld Syndrome
-
Laurence-Moon-Bardet-Biedl Syndrome
-
Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome
-
Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome
-
Patau Syndrome (Trisomy 13)
Risk Factor
Several factors can increase the risk of developing polydactyly, including:
-
Genetic factors
-
Having a family history of polydactyly increases the likelihood.
-
Medical conditions:
-
Children born to mothers with diabetes
-
Babies born with low birth weight (LBW) are at higher risk.
-
Symptoms
The primary visible symptom of polydactyly is the presence of extra digits, meaning the individual may have more than five fingers or toes on their hands or feet. These extra digits are visible from birth. Depending on the type, the extra digits may be fully developed and resemble the other digits. In other cases, they may be underdeveloped and only consist of skin or nerve tissue.
Diagnosis
Polydactyly can be detected in the womb through an ultrasound during routine prenatal checkups. An ultrasound can identify the condition in the first three months of fetal development.
The doctor will ask about your family’s medical history regarding polydactyly and may recommend genetic testing to check for chromosomal abnormalities that could suggest other conditions. If the condition is related to a genetic disorder, the doctor will discuss potential treatment options.
After the baby is born and polydactyly is confirmed visually, if the doctor suspects another genetic condition, further chromosome testing may be recommended. The doctor may also order an X-ray to assess whether the extra digit is attached to bone or just to skin or nerves.
Management
Treatment for polydactyly depends on how the extra digit is attached to the hand or foot. In most cases, the extra digit can be removed by age 2. Surgery is used to ensure the child can use their hands effectively or that their feet can fit comfortably in shoes.
Suture Ligation
If your child has an extra digit, the doctor may recommend a suture ligation procedure. This involves tying a thread or band tightly around the extra digit to cut off its blood flow.
After 1-2 weeks, the digit will fall off naturally. This process does not harm the baby or affect blood flow to the digit or other parts. This method is used if the extra digit does not have bone or other tissue developing with it.
Excision
In this procedure, the doctor removes the extra digit by applying a local anesthetic to the skin and using a cauterizing tool to remove it. Since the baby is under anesthesia, they will not feel pain during the excision, although the anesthetic injection may cause some discomfort. This procedure is suitable if the extra digit lacks bone and is only attached to soft tissue.
Polydactyly Surgery
For polydactyly on the feet, if suture ligation or excision is not an option, surgery may be required. However, surgery is generally not recommended for babies under 1 year old.
Complications
Possible complications from polydactyly treatment include:
-
Bleeding
-
Decreased hand or finger function
-
Skin tears
-
Hallux varus (misalignment of the big toe)
Prevention
You cannot prevent genetic conditions like polydactyly during pregnancy. However, you can minimize risk factors by avoiding harmful substances. Discuss with your doctor the things to avoid during pregnancy, such as:
-
Consuming alcohol
-
Smoking or using tobacco products
-
Drug abuse
When to See a Doctor?
Consult your doctor if you notice any changes in your baby’s hands or feet. After the extra digit is removed, visit your doctor if you notice the following symptoms:
-
Bleeding
-
Discoloration
-
Swelling
-
Discharge
-
Pain and discomfort
Looking for more information about other diseases? Click here!
- dr Hanifa Rahma
Polydactyly. (2022). Retrieved 07 November 2022, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK562295/
Polydactyly. (2021). Retrieved 07 November 2022, from https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003176.htm
What does it Mean if you’re Born with More than Five Fingers on a Hand?. (2018). Retrieved 07 November 2022, from https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/321607
What is Polydactyly. (2019). Retrieved 07 November 2022, from https://www.healthline.com/health/polydactyly
Polydactyly (Extra Digits). (2022). Retrieved 07 November 2022, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24302-polydactyly-extra-digits