Definition
The urine urea nitrogen test measures the level of urea in your urine. This test is commonly used to evaluate kidney function and determine whether the kidneys are functioning properly or if there is an underlying kidney disorder.
Urea is a waste product produced when the body breaks down proteins from the food we consume. As the protein breaks down, nitrogen compounds, including ammonia, are formed. These nitrogen compounds are then converted into urea in the liver. The urea is released into the bloodstream and filtered by the kidneys, ultimately being excreted from the body through urine.
When the kidneys are healthy, they effectively filter and reabsorb necessary substances, while eliminating waste, such as urea, through the urine. A urine urea nitrogen test can help assess the efficiency of kidney function in filtering urea and proteins. If kidney function has decreased, it may indicate kidney disease or other issues. The test is also valuable for diagnosing disorders related to protein absorption or digestion.
Indication
The urine urea nitrogen test is typically recommended for the following purposes:
- To determine the amount of protein consumed by the body.
- For seriously ill patients, this test helps evaluate their protein needs.
- The test helps assess whether the kidneys are working normally or experiencing issues.
- If a patient is undergoing treatment for kidney disorders, this test can help determine if the treatment is effective.
- This test can also help identify conditions that might affect kidney function, such as dehydration, nutritional disorders, or heart failure.
Contraindication
There are no contraindications for the urine urea nitrogen test. It can be performed on most patients without any specific limitations or conditions preventing its use.
Preparation Before the Test
No special preparation is required before the urine urea nitrogen test. You do not need to fast or refrain from eating or drinking prior to the test, and you can continue with your usual activities before and after the test.
However, it is essential to inform your doctor about any medications, vitamins, or supplements you are currently taking, as some medications can influence the test results. Your doctor will provide guidance on whether any of your medications could affect the outcome.
Test Procedure
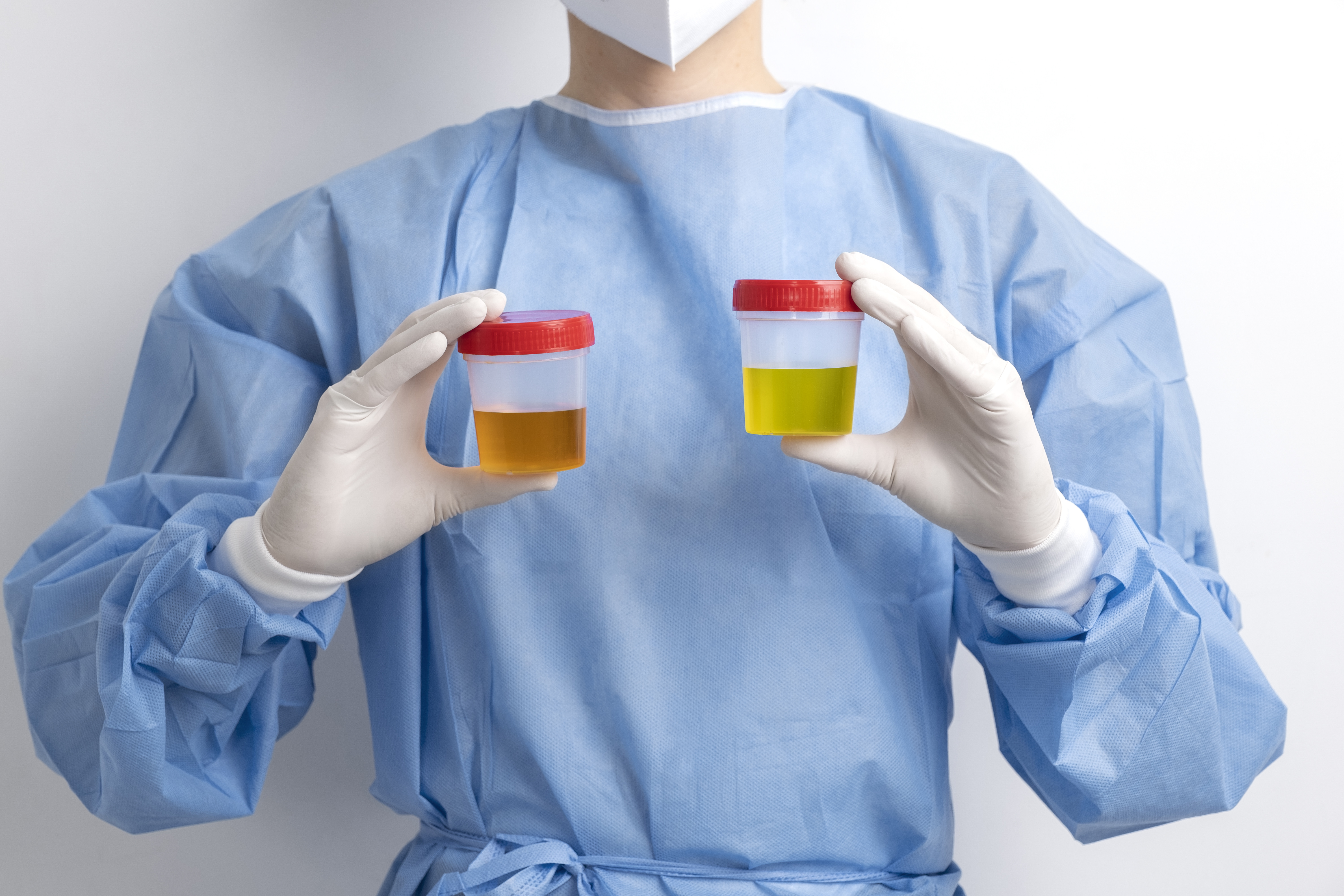
The urine urea nitrogen test involves collecting a urine sample over a 24-hour period. You will be given a special container for urine collection along with instructions on how to collect and store your urine properly.
Begin by noting the time of your first urination in the morning. The first urine should not be collected. For the rest of the day, collect all urine in the provided container. It is important to wash your hands thoroughly before and after collecting each sample. On the second day, collect the morning urine and add it to the container. During this 24-hour period, the urine should be stored in a cool place or a cooler with ice cubes to preserve the sample.
After 24 hours, deliver the container with the urine sample to the laboratory for analysis. There are no risks associated with the urine urea nitrogen test, and it is a non-invasive procedure.
Normal and Abnormal Values
Urine urea levels can vary depending on the laboratory, as each lab may use different machines and reference values. Additionally, factors such as age, gender, and medical history can influence the test results. Therefore, it is important to consult with a doctor regarding your specific test results.
The normal range for urine urea levels is between 12-20 grams per 24 hours, or 428.4-714 mmol per day. Any urine urea levels outside this range are considered abnormal.
Results and Recommendations (Follow-up Tests)
Kidney function tests generally include urea levels, along with creatinine levels and glomerular filtration rate (GFR). If your urea test results are normal and are supported by normal results from other kidney function tests, it suggests that your kidneys are functioning properly. Maintaining your health through a balanced diet, regular water intake, adequate physical activity, and routine health check-ups is recommended.
Abnormal results often point to potential kidney dysfunction. If your urine urea levels are lower than normal, it could indicate:
-
Kidney disorders
-
Malnutrition, particularly from a lack of protein in your daily food intake.
On the other hand, if your urine urea levels are higher than normal, it may suggest:
-
Excessive protein intake from your diet
-
The body breaking down too much protein due to metabolic imbalances.
Consult the Right Doctor
It’s essential to discuss your test results with your doctor to determine an appropriate diet or treatment plan that meets your needs. Your doctor will consider your test results in conjunction with any symptoms or concerns you may have. Depending on your situation, additional tests may be recommended. In addition to a general practitioner, you may also want to consult an internal medicine specialist for further evaluation of your condition.
Looking for more information about laboratory, radiology, and other examination results? Click here!
- dr Hanifa Rahma
Urea Nitrogen Urine Test. (2022). Retrieved 25 November 2022, from https://www.ucsfhealth.org/medical-tests/urea-nitrogen-urine-test
Urine Urea Nitrogen Test. (2018). Retrieved 25 November 2022, from https://www.healthline.com/health/urea-nitrogen-urine
Urea Nitrogen Clearance (Urine). (2022). Retrieved 25 November 2022, from https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?ContentTypeID=167&ContentID=urea_nitrogen_urine