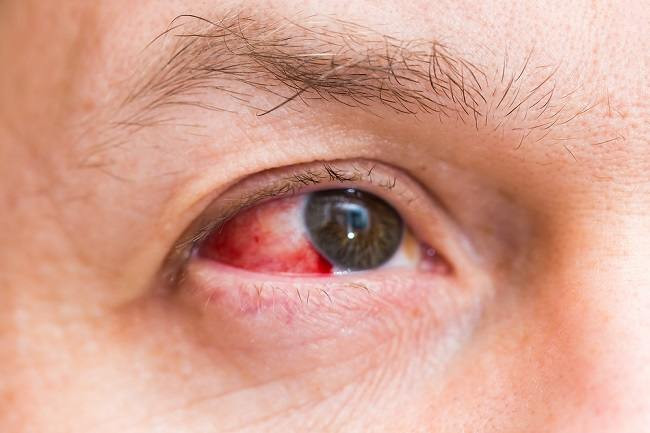
Definition
Burns can occur in the eyes, especially the Philippines. Based on the cause, these burns can be divided into chemical burns and thermal burns. Chemical burns are generally caused by strong acid chemicals or strong bases that are splashed into the eyes. Meanwhile, thermal burns are burns caused by heat. Between these two types of burns, chemical burns are more common.
Cause
Chemical burns are generally caused by strong acid chemical or strong bases. These chemicals can be common household objects found, such as pipe cleaners or ovens, detergents, bleachs, or ammonia. Other chemicals that can cause burns can be fertilizers, acids used in factories, alkaline solutions, limes, and cement. These burns usually occur accidentally, as a result of splashing, snaking, or checking the eyes.
Chemical burns due to bases will usually be more severe than acid. This is due to base properties that easily attach to fat, while fat is the main layer that protects the eye. Not only that, tissue damaged by bases can remove substances that damage protein in the tissue, causing more severe damage. Meanwhile, in burns caused by acid, acid causes protein damage. Damage to this protein causes clots, which further prevents acid from entering the tissue.
Meanwhile, burns from heat can occur due to everyday objects, such as oil during cooking, explosions of electronic cigarettes, electric arcs, or charred wounds. Objects such as fireworks and firecrackers have the possibility to cause chemical and thermal burns at once.
Risk Factors
Chemical and thermal burns are at higher risk for young men and children aged 1-2 years. Young men are often exposed to this substance while working at home, factories, or smoking. Children can be exposed to chemicals and accidentally check their eyes.
Symptoms
In burns, complaints that usually appear are extraordinary pain, watery eyes, stiffness of the temple muscles, and a sharp decline in vision. This usually occurs after exposure to chemical substances, checking the eyes, or being exposed to heat.
Diagnosed
The diagnosis of burns can be done alone based on history. Doctors will usually ask for a history and chronology of the occurrence of short burns. If the burns are caused by chemicals, the doctor will drain infusion fluids into the eyes while monitoring the surface acidity of the eye sphere with lactic paper. If the pH is close to normal, then the doctor will check the eye ball. First, the doctor will enforce it if the eye ball breaks or not. If it breaks, the doctor will refer you to surgery. If it does not break, the doctor will conduct an examination to check the presence of foreign objects or tissue remnants in the eyes. This examination can use dyes to clarify the presence of tissue damage in the cornea. Examination slit lamp it will also be carried out to search for damage to the inside of the eye. Not only that, external checks such as sharp vision and pressure of the eye sphere will be carried out.
In burns due to heat, the doctor will drain infusion into the eye before further examination. The doctor will also ask about the chronology of the trauma incident, and if it involves an explosion, the doctor will examine the eye to look for small particles that stick or penetrate the eye. Examination to look for trauma in other parts of the body is also needed to prevent complications.
Laksana Procedure
Preliminary procedures for burns can be made on its own before arriving at the ER. The most important first aid is to flow in the eyes with clean water to neutralize chemicals or heat. It should be noted that it is better not to use acidic or base chemical to neutralize chemicals, because it can cause more severe damage.
The way to flow the eyes is as follows:
- Fill in the basin with cold clean water
- Put your face in the basin until it touches the water
- Open and close your eyes repeatedly to ensure water touches all parts of the surface of the eye
- Do this for 20-30 minutes while heading to the ER. If not possible, the highest priority is to flow in the eyes with clean water
- In addition to using a basin, you can ask other people for help to drain clean water flowing with a small tube
- Water flow from the nose to the outside
- As long as the water is channeled, blink and move the eyes in all directions to ensure that all the surfaces of the eyes are flowing
- Just like the previous way, this can be done for 20-30 minutes or more
In the ER, doctors usually flow your eyes with infusion after being given a local anesthetic. Doctors can also use tools to hold their eyes open. Usually, doctors will flow their eyes for 30 minutes using 1-3 L of water up to the level of acidity in the neutral eye, which is measured using laxus paper. Doctors will also drain water into the eyelids to ensure the entire surface of the eyes is flowing with water.
Once the acidity level becomes neutral, doctors can prescribe some medications. Antibiotics need to be given to prevent more susceptible infections from occurring due to damage to the surface structure of the eye. The administration of annealing drug for the visual muscles can be used to relieve pain. In addition, doctors can provide artificial tear drops to moisturize the eye surface and relieve pain. Steroids can also be given to reduce inflammation reactions such as swelling and further cornea damage. The use of these drugs must use a doctor's prescription because there are several drugs that should not be given excessive.
In severe cases, emergency room doctors can refer you to an eye specialist for surgery. This advice can be done to prevent further damage or to repair healing.
Complications
Complications that can occur vary. Glaukuma can occur mainly in severe burns, due to fluid flow disturbances in the front eye sphere. In addition, tissue damage can cause dry eyes due to decreased tear production. These damages can also affect eyelids and conjunctive layers, namely the clear layer that coats the eyepieces and inner temples.
Prevention
Chemical and thermal burns are difficult to prevent at daily conditions, but can be prevented at high risk. Use protective glasses while working with chemicals and metals, as this work is at risk of injuring your eyes.
When Do You Have To Go To A Doctor?
Immediately go to the doctor if you experience the following symptoms after exposure to heat or chemicals:
- Double or decreased views that are not lost by flickering
- Eye pain
- Uncomfortable when looking at the light source
- The sensation of foreign objects in the eyes
- Red eyes, swelling, drizzling, watery, or pusy
- The above symptoms occurred for more than 24 hours
- The above symptoms occur too often or get worse
Want to know more about other diseases? Check here, yes!
- dr Ayu Munawaroh, MKK
Bates, A., & Zanaboni, A. (2021). Ocular Burns. Retrieved 24 October 2021, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459221/.
Seltman, W. (2020). Eye Burns/Corneal Burns Treatment. Retrieved 24 October 2021, from https://www.webmd.com/first-aid/corneal-flash-burns-treatment.
Trief, D., Woodward, M., Murchison, A., Auran, J., & Syed, Z. (2021). Chemical (Alkali and Acid) Injury of the Conjunctiva and Cornea - EyeWiki. Retrieved 24 October 2021, from https://eyewiki.aao.org/Chemical_(Alkali_and_Acid)_Injury_of_the_Conjunctiva_and_Cornea.