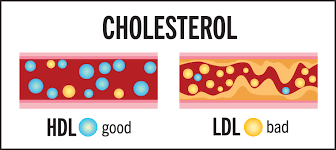
Definisi
Pemeriksaan kolesterol total merupakan salah satu jenis pemeriksaan kadar kolesterol untuk memeriksa kadar lipid atau substansi lemak dalam darah. Kadar lipid dalam darah merujuk pada kolesterol “jahat” (LDL), kolesterol “baik” (HDL), dan lemak trigliserida. Oleh karena itu, pemeriksaan kolesterol total akan menghitung total dari kadar tiga jenis kolesterol yang ada di dalam darah.
Pemeriksaan kolesterol total diasosiasikan dengan penyakit dislipidemia, rutin dijalankan untuk melihat bila ada kelainan metabolisme lemak dalam darah. Kondisi dislipidemia itu sendiri bisa muncul karena adanya kelainan genetik atau terjadi akibat adanya penyakit lain, seperti:
- Gangguan ginjal
- Diabetes
- Penyakit kardiovaskuler (jantung dan pembuluh darah) yang terpicu karena pembentukan plak lemak
- Sindrom metabolik (kombinasi dari obesitas, diabetes, dan tekanan darah tinggi)
Indikasi
Pemeriksaan ini dilakukan pada kondisi sebagai berikut:
- Pasien yang dicurigai mengalami dislipidemia
- Sebagai estimasi risiko kardiovaskuler pada pasien
- Screening atau penyaringan profil lemak yang diperiksa secara rutin
- Salah satu parameter terapi sekunder bagi pasien dengan risiko kardiovaskular tinggi
Kontraindikasi
Tidak ada kontraindikasi, penyakit atau kondisi medis tertentu yang membuat seseorang tidak bisa melakukan pemeriksaan ini.
Persiapan Sebelum Pemeriksaan
Tidak ada persiapan khusus sebelum melakukan pemeriksaan kolesterol total. Pemeriksaan ini bisa dilakukan dalam keadaan tidak berpuasa serta bisa dilakukan kapan saja.
Prosedur Pemeriksaan
Pemeriksaan kolesterol total menggunakan sampel serum darah sebanyak 0,5 ml. Sampel serum darah ini diambil dari pembuluh darah vena dan akan dikumpulkan ke dalam tabung khusus. Petugas laboratorium akan memakai sarung tangan khusus dan APD (Alat Pelindung Diri) saat mengambil sampel pemeriksaan.
Sebelum mengambil darah, petugas akan memasang pita elastis dan membersihkan area penusukan jarum dengan kasa antiseptik. Biasanya petugas mengambil darah di area lipatan siku. Setelah darah diambil dan dimasukkan ke dalam tabung khusus, petugas akan melepas pita elastis yang terpasang, menekan dan membersihkan area penusukan dengan kasa antiseptik. Prosedur pemeriksaan ini hanya berlangsung selama beberapa menit saja.
Nilai Normal dan Abnormal
Berbeda dengan nilai kolesterol HDL yang dibedakan berdasarkan jenis kelamin, rentang nilai normal kolesterol total hanya dibedakan berdasarkan usia. Secara umum berikut rentang nilai normal dan abnormal pada hasil pemeriksaan kolesterol total:
Pada Orang Dewasa:
|
Nilai (mg/dL) |
Interpretasi |
|
<200 |
Normal |
|
200-239 |
Sedikit Tinggi (Borderline) |
|
>240 |
Tinggi |
|
>310 |
Diduga Hiperkolesterolemia Familial |
|
>500 |
Diduga Dislipidemia Monogenik |
Pada Anak-Anak (18 Tahun ke Bawah):
|
Nilai (mg/dL) |
Interpretasi |
|
<170 |
Normal |
|
170-199 |
Sedikit Tinggi (Borderline) |
|
≥200 |
Tinggi |
Hasil dan Saran (Pemeriksaan Lanjutan)
Normal
Jika hasil pemeriksaan kolesterol total Anda menunjukkan nilai normal, kemungkinan besar Anda telah menjalankan pola hidup sehat dengan baik. Asosiasi Jantung Amerika Serikat (AHA) menyarankan untuk orang dewasa sejak usia 20 tahun, pemeriksaan kolesterol rutin dilakukan setiap 4-6 tahun sekali, karena pada usia ini lah kadar kolesterol darah mulai meningkat.
Pusat Pengendalian dan Pencegahan Penyakit Amerika Serikat (CDC) juga menyarankan pemeriksaan kolesterol pada anak setidaknya dilakukan 2 kali yaitu pada usia 9-11 tahun dan 17-21 tahun. Sedangkan anak dengan faktor risiko Diabetes, Obesitas, atau ada keluarga yang mengalami penyakit kolesterol tinggi (Dislipidemia), harus diperiksakan kadar kolesterolnya pada usia 2-8 tahun dan 12-16 tahun.
Sedikit Tinggi
Jika hasil pemeriksaan kolesterol total Anda menunjukkan nilai sedikit tinggi, perlu dilihat kembali ke belakang apakah persiapan puasa selama 8-14 jam sebelum pemeriksaan sudah dilakukan dengan baik. Angka 8-14 jam bervariasi di setiap laboratorium dikarenakan pada perbedaan mesin pemeriksaannya. Umumnya 10-12 jam ialah waktu yang optimal untuk berpuasa makan dan minum (selain air putih) sebelum pemeriksaan. Jika Anda tidak yakin, Anda dapat mengulang kembali pemeriksaan kolesterol.
Nilai kolesterol total digunakan untuk mengestimasi risiko kardiovaskular atau penyakit jantung dan pembuluh darah secara keseluruhan. Jika nilai kolesterol total Anda atau anak Anda sedikit tinggi sebaiknya konsultasikan dengan dokter. Dokter akan mempertimbangkan kondisi kesehatan Anda berdasarkan pemeriksaan profil lipid lainnya seperti nilai trigliserida, kolesterol LDL dan HDL.
Tinggi
Jika hasil pemeriksaan kolesterol total Anda menunjukkan nilai tinggi, sebaiknya Anda berkonsultasi dengan dokter. Kemungkinan dokter akan menyarankan perubahan pola makan dan gaya hidup menjadi lebih sehat, atau bahkan juga memulai terapi obat untuk membantu menurunkan nilai kolesterol Anda. Mengacu pada Pedoman Pengelolaan Dislipidemia di Indonesia, mengurangi asupan lemak jenuh dan lemak trans, serta meningkatkan asupan makanan yang mengandung fitosterol ialah cara terbaik untuk menurunkan kadar kolesterol total dan kolesterol LDL. Selain itu, meningkatkan asupan serat, menurunkan berat badan jika berlebih, dan meningkatkan aktivitas fisik juga berpengaruh pada penurunan kadar kolesterol total dan HDL.
Jika hasil pemeriksaan kolesterol total Anda menunjukkan nilai sangat tinggi, melebihi 310 mg/dL, dokter akan mencurigai adanya kemungkinan penyakit genetik seperti Hiperkolesterolemia Familial Homozigot (HoFH) atau Dislipidemia Monogenik. Penyakit ini jarang terjadi dan sangat mengancam nyawa.
Konsultasikan ke Dokter yang Tepat
Hasil pemeriksaan kolesterol total pada orang dewasa dapat dikonsultasikan dengan dokter umum, untuk selanjutnya dilakukan pemeriksaan lanjutan ataupun memulai terapi untuk diagnosis yang sesuai. Anda juga dapat berkonsultasi dengan dokter jantung, dokter penyakit dalam atau konsultan Endokrinologi untuk berdiskusi mengenai masalah kolesterol Anda lebih jauh. Pada pasien anak, hasil pemeriksaan selain normal harus dikonsultasikan dengan dokter spesialis anak.
Mau tahu informasi seputar hasil pemeriksaan laboratorium, radiologi, dan lainnya? Cek di sini, ya!
- dr Hanifa Rahma
Aman AM, Soewondo P, Soelistijo SA, et al. Pedoman Pengelolaan Dislipidemia di Indonesia. PB Perkeni. 2019
Erwinanto, Santoso A, Putranto JNE, et al. Panduan Tata Laksana Dislipidemia. Perhimpunan Dokter Spesialis Kardiovaskular Indonesia. 2017
Grundy S, Stone N, Bailey A. et al. AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. 2018. Circulation, 139(25). doi: 10.1161/cir.0000000000000625
AHA. What Your Cholesterol Levels Mean. Heart.org. 2020 Nov. https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/cholesterol/about-cholesterol/what-your-cholesterol-levels-mean
CDC. How and When to Have Your Cholesterol Checked. 2021 April. https://www.cdc.gov/features/cholesterol-screenings/index.html


/6302127de0c5c.jpeg)