Definition
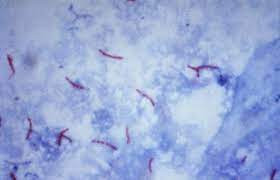
The Acid Fast Bacillus (AFB) test is a diagnostic laboratory procedure used to detect tuberculosis (TB) caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This bacteria primarily affects the lungs but can also target other organs. TB is an airborne disease, transmitted when infected individuals release bacteria into the air through coughing or sneezing. The term "acid-fast" refers to the bacteria's ability to resist decolorization by acid during laboratory testing, which is why the test is named as such.
The AFB test is most commonly used to identify pulmonary tuberculosis (TB of the lungs), as sputum samples are typically collected for analysis. In some cases, the test may also be performed on blood, stool, urine, or bone marrow samples to check for TB infection outside the lungs.
AFB testing is often performed alongside other diagnostic tests, such as complete blood counts (CBC), chest X-rays, and clinical evaluations to help determine the cause of symptoms like fever, persistent cough, and weight loss.
Indication
The AFB test, particularly with sputum samples, is crucial in diagnosing pulmonary TB. If you are suspected of having TB, your doctor may ask you to cough up sputum samples at specific intervals for testing. These samples are collected in a sterile container provided by the laboratory. If you have difficulty coughing up sputum, your doctor may prescribe medications to help induce coughing. In more complex cases, a bronchoscopy (a procedure to collect sputum from deeper in the lungs) may be performed if pulmonary TB is strongly suspected.
AFB tests are generally recommended if you present with symptoms suggestive of pulmonary TB, such as a persistent fever lasting more than 3 days, coughing up phlegm or blood, chest pain, unexplained weight loss, night sweats and weakness, loss of appetite and chills. For patients already diagnosed with pulmonary TB, the AFB test can be used to monitor disease progression and assess the effectiveness of treatment. It can also help detect any new or persistent infections.
Additionally, the AFB test is often used as a screening test for close contacts of TB patients. If other members of the household or community have been exposed to TB, the AFB test can help detect early signs of infection, ensuring that those who are infected receive timely treatment and care. This is particularly important in preventing the further spread of the disease.
Contraindication
There are no contraindications or specific conditions that prevent an individual from undergoing the AFB test. It is a generally safe procedure for most people.
Preparation Before the Test
Before undergoing the AFB test, there are a few preparations that need to be followed for accurate results. First, it is important not to eat or drink immediately after waking up in the morning. Upon waking up, it is recommended to brush your teeth to clean your mouth. After brushing, you should proceed to clear your throat and cough up phlegm, which will then be collected in a sterile container, usually a special pot provided by the healthcare facility.
Test Procedure
The AFB test typically uses sputum samples for analysis. You will be asked to bring a sterile pot to collect the sputum sample. To collect a good sample, you will first be asked to take a deep breath and hold it for three to five seconds. After holding your breath, exhale slowly. This process will be repeated until you feel the urge to cough. Once you are able to cough up the phlegm, you will spit it into the sterile container. Afterward, the container should be tightly closed to avoid contamination.
The sputum sample is typically collected in two instances. The first collection will be done at the time the doctor requests the sample. The second sample will be collected the next morning in a new pot. Both samples should be delivered to the laboratory as soon as possible.
When the laboratory technician receives the sputum samples, they will first assess the quality of the samples. It is important that the sample primarily contains sputum rather than saliva to ensure the accuracy of the test. The laboratory staff will also use personal protective equipment (PPE) when handling the sample to prevent exposure to the bacteria.
A microscope and glass slides will be used to evaluate the sputum sample. The laboratory will follow the established protocols for identifying Acid Fast Bacillus (AFB) under the microscope.
Normal and Abnormal Values
The results of the AFB test are categorized based on the presence of AFB in the sputum sample. There is no distinction between age or gender in the interpretation of results.
|
Value |
Interpretation |
|
Not found |
Negative |
|
+1; +2; +3: +4 |
Positive |
Results and Recommendations (Follow-up Tests)
Negative Results
If your AFB test results come back negative, it suggests that you are healthy and not infected with tuberculosis, provided you do not exhibit symptoms related to TB.
If you have no specific symptoms or clinical signs of tuberculosis, it is advisable to maintain your healthy lifestyle to prevent any risk of infection.
Positive Results
If the AFB test shows positive results, it means that you are currently infected with the AFB bacteria. If you have symptoms consistent with pulmonary TB, such as a prolonged cough, coughing up blood, weight loss, fever, or night sweats, and you also have a positive result from the AFB test, it is likely that you have pulmonary tuberculosis.
In this case, your doctor will recommend further testing to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the infection. Additional tests may include:
-
Chest X-ray: To evaluate the lungs and detect any damage caused by TB.
-
Complete blood count (CBC): To check your overall health, including red and white blood cells, and assess for infection or other underlying conditions.
-
Liver function tests: To monitor liver health, as TB medications can sometimes affect the liver.
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, a specific treatment regimen will be prescribed. It's important to follow the prescribed treatment diligently to avoid the development of drug-resistant TB.
In addition to medical treatment, you are advised to adopt a healthy lifestyle, including eating a balanced and nutritious diet, exercising regularly, managing stress, and avoiding smoking or alcohol consumption.
Consult the Right Doctor
For adults, positive AFB test results should be discussed with a general practitioner or a pulmonologist (lung specialist) to begin appropriate treatment. An internist may also be consulted if necessary. For pediatric patients, it is essential to consult with a pediatrician to ensure proper diagnosis and care.
Looking for more information about laboratory, radiology, and other examination results? Click here!
- dr Hanifa Rahma
Medscape. Tuberculosis (TB) workup. 2020 June. Retrieved 25 April 2022, from https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/230802-workup#c1
National Library of Medicine. Acid fast bacteria. 2021 August. Retrieved 25 April 2022, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537121/
Missouri Department of Healt & Senior Services. Acid-fast bacilli (AFB) smear and culture. 2022 April. Retrieved 25 April 2022, from https://health.mo.gov/lab/smearculture.php
Medline Plus. Acid-fast bacillus (AFB) test. 2021 September. Retrieved 25 April 2022, from https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/acid-fast-bacillus-afb-tests/