Definition
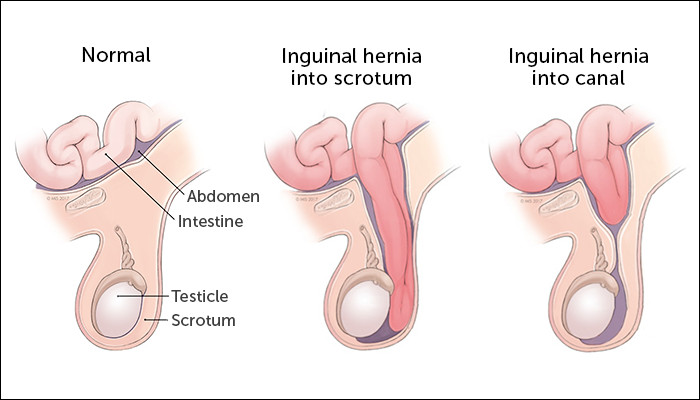
Scrotal hernia is the protrusion of tissue from the abdomen—such as a part of the intestine—into the scrotum (testicular sac) through a weakened inguinal canal (a passage in the groin area).
Causes
Scrotal hernia occurs when there is a weak spot in the inguinal canal, where the spermatic cord (a structure resembling a cord that contains blood vessels, nerves, and a duct that carries sperm from the testicles) enters the scrotum.
This condition can occur due to:
- Increased pressure in the abdomen
- A weak spot in the abdominal wall
- Frequent straining during bowel movements or urination
- Heavy lifting
- Pregnancy
- Chronic coughing or sneezing
Risk Factor
Factors contributing to the occurrence of scrotal hernia include:
- Weakening of abdominal wall muscles with age
- White ethnicity is more prone to hernias
- Family history. If a patient has a close family member, such as a parent or sibling, with a hernia, the risk of developing a hernia increases
- Long-term cough, such as due to tuberculosis or smoking
- Prolonged constipation. Constipation causes straining during bowel movements, increasing abdominal pressure, which raises the risk of hernia
- Premature birth or low birth weight. Scrotal hernia is more common in people born prematurely or with low birth weight
- History of hernia or previous hernia repair surgery. Even if a patient had a hernia during childhood, they still have a higher risk of developing another hernia later
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of scrotal hernia include:
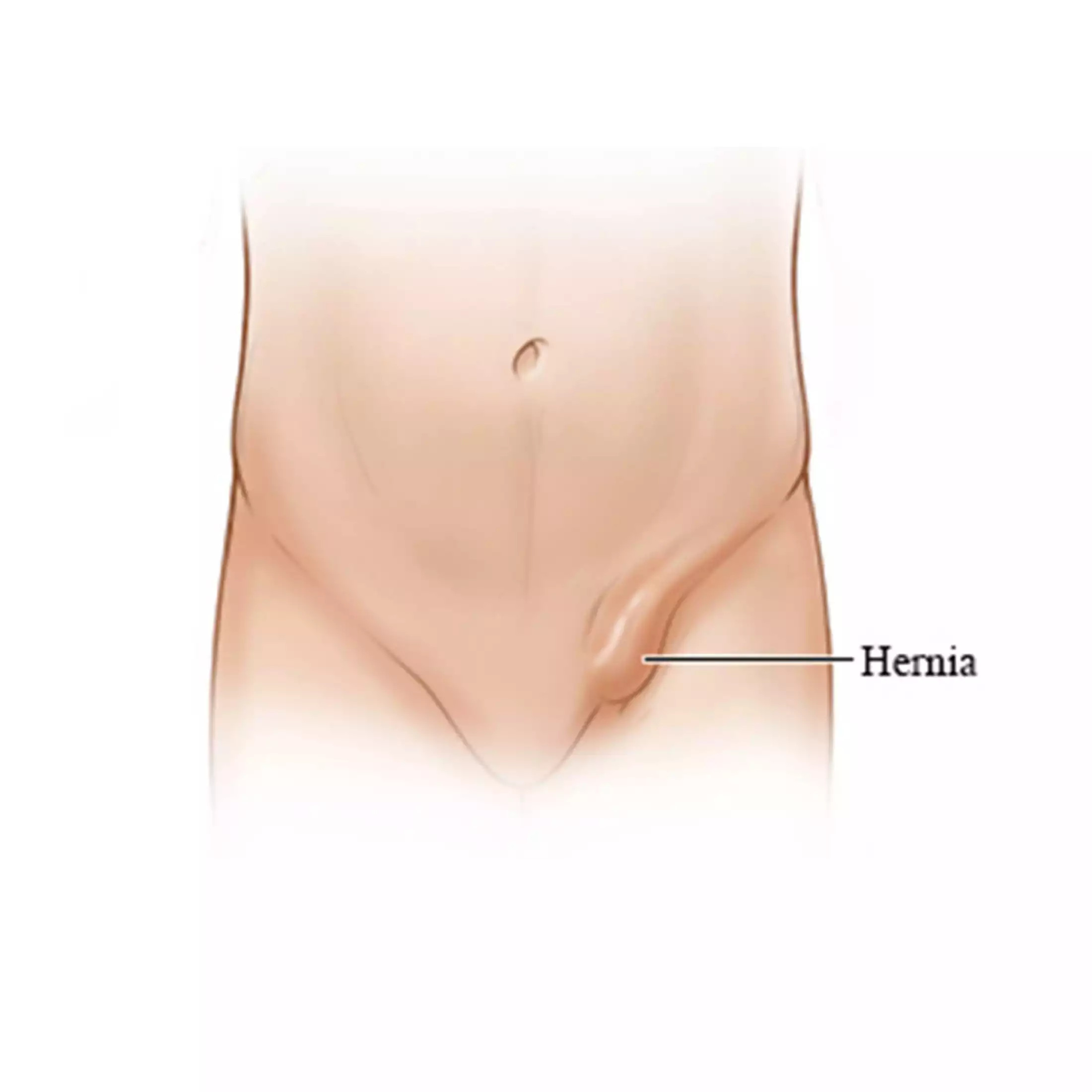
- A lump in one of the testicles, which becomes more noticeable when the patient stands, sits, or particularly when coughing or straining
- A burning sensation or pain in the lump
- Pain or discomfort in the scrotum that may extend to the groin, especially when bending over, coughing, or lifting heavy objects. However, many hernias do not cause pain
- A sensation of heaviness or pulling in the testicular area
- Sometimes, pain and swelling can occur around the testicles
Scrotal hernia can also occur in newborns and children due to a congenital weakness in the abdominal wall. Sometimes, the hernia is only visible when the baby cries, coughs, or strains during bowel movements. The baby may appear fussier and have a reduced appetite compared to usual.
In older children, the hernia becomes more noticeable when the child coughs, strains during bowel movements, or stands for a long time.
Diagnosis
A physical examination is usually sufficient to diagnose a scrotal hernia. The doctor will examine the lump in the patient’s scrotum. Since standing and coughing can make the hernia more prominent, the patient may be asked to stand and cough or strain.
If the diagnosis is still unclear, the doctor may perform radiological examinations such as ultrasonography (USG), CT scan, or MRI.
Management
Here are treatments and therapies for scrotal hernia. If the hernia is small and not bothersome, the doctor may recommend just monitoring it. Sometimes, wearing a supportive device can help alleviate symptoms, but it is essential to consult a doctor to ensure proper use.
The doctor may try manual pressure to push the lump back in in children before considering surgery. Large or painful hernias usually require surgery to reduce symptoms and prevent serious complications.
There are two common types of hernia surgery: open hernia repair and minimally invasive hernia repair.
- Open hernia repair: In this surgery, local anesthesia with sedation or general anesthesia is used. The doctor makes an incision in the groin and pushes the protruding tissue back into the abdomen. The weak area is then sewn up, often with the addition of synthetic mesh (hernioplasty). The incision is then closed with stitches, staples, or surgical glue. After surgery, the patient is encouraged to move as soon as possible, but it may take several weeks before they can return to normal activities.
- Minimally invasive hernia repair: This surgery requires general anesthesia. The doctor operates through several small incisions in the abdomen using laparoscopic or robotic tools to repair the hernia. Gas is used to inflate the abdomen, making internal organs more visible. A small tube with a tiny camera (laparoscope) is inserted into one incision. Guided by the camera, the doctor inserts small instruments through other small incisions to repair the hernia using mesh. People undergoing this procedure usually experience less pain and scarring after surgery and can return to normal activities more quickly.
Complications
Hernias are not entirely harmless and can lead to life-threatening complications.
Complications of scrotal hernia include:
- Pressure on surrounding structures: A large hernia in the scrotum can cause pain and swelling in the surrounding area
- Incarcerated hernia: If a hernia cannot be pushed back into place, the hernia contents can become trapped at the weak point in the groin canal. This causes severe pain, nausea, vomiting, and an inability to pass stool or gas
- Strangulated hernia: An incarcerated hernia can become strangulated when the blood flow to the trapped tissue is cut off, depriving the tissue of oxygen and nutrients. Strangulation can cause tissue death in the trapped intestine. This is a life-threatening condition requiring emergency surgery.
Signs and symptoms of a strangulated hernia include:
- Nausea, vomiting, or both
- Fever
- Sudden pain that intensifies rapidly
- A hernia bulge that turns red, purple, or dark
- Inability to pass stool or gas
Prevention
While congenital weakness in the abdominal muscles that predisposes someone to scrotal hernia cannot be prevented, you can reduce pressure on the abdominal muscles by:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Consult a doctor about the best exercise and diet plan for you
- Increasing high-fiber foods: Fruits, vegetables, and whole grains contain fiber that helps prevent constipation and straining
- Being careful when lifting heavy objects or avoiding lifting heavy objects: If you must lift heavy objects, always lift from the knees, not the waist
- Quitting smoking: Besides its impact on various serious diseases, smoking often causes chronic cough, which can lead to or trigger a hernia
When to See a Doctor?
You or your child should seek immediate medical help if a hernia bulge becomes red, purple, or dark, or if you notice signs or symptoms of a strangulated hernia.
You should also consult a doctor if you or your child has a painful or visible bulge in one of the testicles. The bulge will be more noticeable when standing; you can usually feel it when placing your hand over it.
Looking for more information about other diseases? Click here!
- dr. Alvidiani Agustina Damanik
Inguinal hernia - Symptoms and causes. (2022). Retrieved 30 September 2022, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/inguinal-hernia/symptoms-causes/syc-20351547
Inguinal Hernia: Types, Causes, Symptoms & Treatment. (2022). Retrieved 30 September 2022, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16266-inguinal-hernia
Inguinal hernia repair. (2022). Retrieved 30 September 2022, from https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/inguinal-hernia-repair/