Definition
A triglyceride test is a medical examination used to assess the level of triglycerides in the blood.
Triglycerides are a type of fat that circulates in the bloodstream with the help of proteins. They are produced when the body converts excess calories into fat. When the body has surplus calories that are not immediately needed for energy, these calories are stored as triglycerides in fat cells. Triglycerides can later be used as an additional source of energy when the body requires it, such as during physical activities or exercise.
Triglyceride levels typically rise when the intake of calories exceeds the amount used by the body (for instance, from consuming high-calorie foods or beverages without expending enough energy through physical activity).
High triglyceride levels can be attributed to several factors, including smoking, lack of exercise, obesity, excessive alcohol consumption, and a diet low in protein and high in carbohydrates.
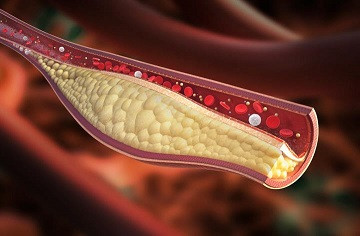
Elevated triglyceride levels are closely associated with an increased risk of coronary heart disease and are considered one of the clinical markers of a condition known as metabolic syndrome.
Indications
This test is typically performed under several conditions, including the following:
-
To assist in diagnosing dyslipidemia (elevated cholesterol levels in the body) or metabolic syndrome (a group of conditions linked to metabolic disorders).
-
To monitor the effectiveness of treatment for dyslipidemia or metabolic syndrome.
-
As part of routine screening during medical check-ups (MCU).
-
To assess risk factors for coronary heart disease.
-
To evaluate markers of pancreatic inflammation (pancreatitis).
Contraindication
There are no contraindications or conditions that would prevent someone from undergoing this test.
Preparation Before the Test
Special preparation is required before performing a triglyceride test, specifically fasting for at least 12 hours. Additionally, patients are advised to avoid consuming alcoholic beverages for 24 hours prior to the test.
It is also recommended to consult with a doctor before undergoing a triglyceride test, as certain factors may affect laboratory results and prevent them from reflecting your true condition.
Test Procedure
The triglyceride test generally requires a blood serum sample of 0.25 - 0.5 ml, which is drawn from a vein and collected into a specialized tube. Laboratory staff will wear appropriate gloves and personal protective equipment (PPE) when collecting the sample.
Before the blood is drawn, the technician will apply an elastic band around the arm and disinfect the needle puncture area with antiseptic gauze. Typically, the blood is drawn from the area near the elbow crease. Once the blood has been collected in the special tube, the elastic band is removed, and the puncture site is pressed and cleaned with antiseptic gauze. This procedure is quick, usually taking only a few minutes. The blood sample will then be analyzed using specialized equipment in the laboratory, and results are typically available within a few hours.
Normal and Abnormal Values
The normal triglyceride value range varies by age and gender. In general, the following are the normal and abnormal value ranges for triglyceride test results:
In adults, both men and women:
|
Value (mg/dL) |
Interpretation |
|
<150 |
Normal |
|
150 - 199 |
Slightly high |
|
200 - 499 |
High |
|
>500 |
Very high |
In children aged 2-17 years, based on the Expert Panel on Integrated Guidelines for Cardiovascular Health and Risk Reduction in Children and Adolescents, the laboratory value ranges for triglycerides are as follows:
For children aged 2-9 years:
|
Value (mg/dL) |
Interpretation |
|
<75 |
Normal |
|
75-99 |
Slightly high |
|
>100 |
High |
For children aged 10-17 years
|
Value (mg/dL) |
Interpretation |
|
<90 |
Normal |
|
90 - 129 |
Slightly high |
|
>130 |
High |
However, it’s important to note that each laboratory may have slightly different reference ranges based on the equipment or methods they use.
Results and Recommendations (Follow-up Tests)
Normal Results
If your triglyceride test results fall within the normal range, it suggests that you are likely maintaining a healthy lifestyle. To continue this, it’s recommended to sustain your current lifestyle to help prevent diseases associated with high triglyceride levels, such as coronary heart disease and metabolic syndrome.
Slightly High Results
If your triglyceride test results indicate slightly elevated values, you should review whether you followed the proper fasting protocol before the test, which generally requires at least 12 hours of fasting. Ideally, fasting for 10 hours is considered optimal, and only water should be consumed during this time. If you are unsure whether the fasting was done correctly, you can repeat the triglyceride test.
Triglyceride levels are an important indicator of overall cardiovascular or heart and blood vessel health. If your triglyceride values are slightly elevated, also known as moderate hypertriglyceridemia, it is essential to consult a doctor. The doctor will assess your health status by considering other lipid profile tests, such as total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and HDL cholesterol, to get a clearer understanding of your cardiovascular risk.
High Results
If your triglyceride test results show high values, it is strongly recommended to consult with a doctor. The doctor will likely suggest dietary and lifestyle changes to improve your health, and may also initiate drug therapy to help lower your triglyceride levels.
Several factors and medical conditions contribute to high triglyceride levels in the blood, such as obesity, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, thyroid disorders, uncontrolled type 2 diabetes mellitus, and liver or kidney disease.
According to the Dyslipidemia Guidelines, several strategies for lowering triglyceride levels include adopting a healthy lifestyle. This involves avoiding high-fat foods and drinks, drinking plenty of water (at least 2 liters per day), and engaging in light physical activities like jogging or walking for 30-60 minutes, 3-5 times a week.
Very High Results
If your triglyceride test results show very high values, it is crucial to consult a doctor immediately. Very high triglyceride levels, known as severe hypertriglyceridemia, can lead to inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention. The doctor will evaluate your situation and may prescribe specific medications to lower your triglyceride levels.
Consult the Right Doctor
Triglyceride test results in adults should be discussed with a general practitioner for further tests or to initiate therapy for an accurate diagnosis. You can also consult a cardiologist, internist, or metabolic-endocrine specialist to explore your triglyceride issues in more depth. For pediatric patients, any abnormal test results should be reviewed with a pediatrician or a subspecialist in pediatric metabolic-endocrinology to determine the exact cause.
Looking for more information about laboratory, radiology, and other examination results? Click here!
- dr Hanifa Rahma
Medscape. Lipid profile (triglycerides). 2021 November. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2074115-overview#a1
Aman AM, Soewondo P, Soelistijo SA, et al. Pedoman Pengelolaan Dislipidemia di Indonesia. PB Perkeni. 2019
CDC. How and When to Have Your Cholesterol Checked. 2021 April. https://www.cdc.gov/features/cholesterol-screenings/index.html
Medline Plus. 2021 September. https://medlineplus.gov/triglycerides.html
Medline Plus. 2020 July. https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/triglycerides-test/
Mayo Clinic Staff. Triglycerides: why do they matter. 2022 April. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-cholesterol/in-depth/triglycerides/art-20048186
Mayo Clinic Labs. Triglycerides. 2022 April. https://www.mayocliniclabs.com/test-catalog/overview/8316#Specimen


/6302127de0c5c.jpeg)