Definisi
Pemeriksaan transferin adalah pemeriksaan yang berfungsi untuk mengetahui kadar protein transferin di dalam darah. Transferin merupakan salah satu protein yang dihasilkan oleh organ hati. Transferin berfungsi untuk mengikat dan membawa zat besi ke seluruh tubuh.
Ketika cadangan zat besi di dalam tubuh mulai berkurang atau menipis, hati akan memproduksi lebih banyak transferin untuk memenuhi kebutuhan zat besi ke dalam darah. Hampir seluruh zat besi di dalam tubuh terikat dengan transferin.
Zat besi memiliki berbagai peranan penting dalam tubuh, termasuk membantu sel darah merah membawa oksigen ke seluruh tubuh. Kelebihan maupun kekurangan zat besi dapat menyebabkan berbagai masalah kesehatan yang cukup serius bila tidak diatasi dengan tepat.
Tubuh tidak dapat memproduksi zat besi sendiri. Zat besi bisa didapatkan melalui makanan yang dikonsumsi maupun dari suplemen. Beberapa makanan yang mengandung zat besi antara lain telur, daging, hati sapi, bayam, dan kacang-kacangan.
Indikasi
Dokter dapat menyarankan untuk melakukan pemeriksaan transferin jika Anda mengalami gejala anemia akibat kekurangan zat besi atau pada pemeriksaan darah lainnya (seperti darah lengkap, pemeriksaan feritin, TIBC dan serum iron) Anda diduga mengalami anemia akibat kekurangan zat besi.
Selain itu, pemeriksaan ini juga dapat direkomendasikan oleh dokter jika Anda memiliki gejala kelebihan zat besi (seperti hemokromatosis, suatu kelainan genetik yang menyebabkan penumpukan zat besi di tubuh).
Berikut gejala jika Anda mengalami kekurangan zat besi:
- Kulit pucat
- Kelelahan dan lemas
- Mudah sakit
- Sering merasa kedinginan
- Pusing, napas pendek dan jantung berdetak lebih cepat
Namun, jika tubuh mengalami kelebihan zat besi dapat menimbulkan gejala:
- Nyeri sendi
- Nyeri perut
- Mudah lelah
- Merasa lemah
Pemeriksaan transferin juga mungkin dibutuhkan dokter untuk menilai keberhasilan pengobatan pada kasus kelebihan maupun kekurangan zat besi.
Kontraindikasi
Tidak ada kontraindikasi atau kondisi yang membuat seseorang tidak bisa melakukan pemeriksaan transferin.
Persiapan Sebelum Pemeriksaan
Pemeriksaan transferin tidak membutuhkan persiapan khusus selain berpuasa. Anda akan diminta untuk berpuasa (tidak makan) selama kurang lebih 12 jam sebelum pemeriksaan dilakukan. Umumnya, pemeriksaan ini dilakukan di pagi hari.
Terdapat beberapa jenis obat-obatan yang dapat memengaruhi hasil pemeriksaan transferin. Informasikan pada dokter bila Anda mengonsumsi obat-obatan tertentu seperti:
- Antasida
- Obat kontrasepsi atau obat yang mengandung esterogen/testosteron
- Antibiotik
- Aspirin
- Suplemen zat besi
Dokter akan memberitahu Anda apakah perlu memberhentikan sementara waktu mengonsumsi obat-obatan tersebut. Jangan tiba-tiba berhenti mengonsumsi obat tanpa memberitahu dokter terlebih dahulu.
Perempuan yang sedang menstruasi biasanya memiliki kadar zat besi lebih rendah, sehingga mungkin dapat memengaruhi hasil dari pemeriksaan ini. Konsultasikan ke dokter jika Anda memiliki kondisi medis tertentu yang mungkin dapat mengganggu hasil laboratorium sehingga tidak menggambarkan kondisi Anda yang sesungguhnya.
Prosedur Pemeriksaan
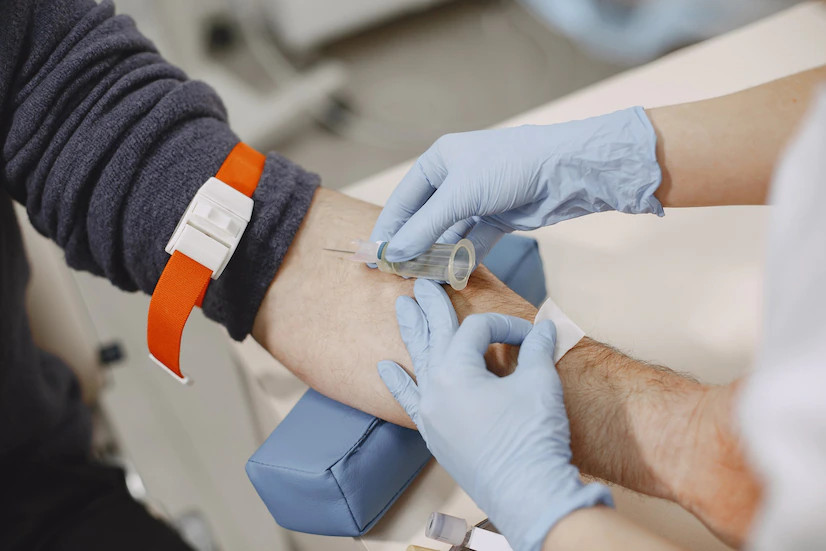
Pemeriksaan transferin umumnya menggunakan sampel serum darah sebanyak 0,25-0,5 ml. Sampel serum darah ini diambil dari pembuluh darah vena dan akan dikumpulkan ke dalam tabung khusus. Petugas laboratorium akan memakai sarung tangan khusus dan APD (Alat Pelindung Diri) saat mengambil sampel pemeriksaan.
Sebelum mengambil darah, petugas akan memasang pita elastis dan membersihkan area penusukan jarum dengan kasa antiseptik. Biasanya petugas mengambil darah di area lipatan siku. Setelah darah diambil dan dimasukkan ke dalam tabung khusus, petugas akan melepas pita elastis yang terpasang, menekan dan membersihkan area penusukan dengan kasa antiseptik.
Prosedur pemeriksaan ini hanya berlangsung selama beberapa menit saja. Sampel darah yang telah didapatkan akan diperiksakan menggunakan alat khusus di laboratorium, dan hasilnya bisa diketahui dalam beberapa jam kemudian.
Baca Juga: Pemeriksaan Feritin - Indikasi, Prosedur, dan Hasil Pemeriksaan | AI Care (ai-care.id)
Nilai Normal dan Abnormal
Secara umum, berikut ini merupakan rentang nilai normal dan abnormal pada hasil pemeriksaan transferin.
| Nilai (mcg/dL) |
Interpretasi |
| < 215 |
Rendah |
| 215 - 380 |
Normal |
| > 380 |
Tinggi |
Meskipun demikian, setiap laboratorium memiliki rentang nilai yang sedikit berbeda antara satu laboratorium dengan laboratorium lainnya sebab bergantung pada alat atau mesin yang digunakannya.
Hasil dan Saran (Pemeriksaan Lanjutan)
Rendah
Hasil pemerikaan transferin yang rendah menandakan tubuh memiliki sedikit transferin untuk mengikat zat besi, dengan kata lain tubuh memiliki kadar zat besi bebas yang tinggi di dalam darah.
Beberapa kondisi yang bisa menyebabkan kadar zat besi tinggi, diantaranya:
- Keracunan zat besi atau timbal
- Sirosis hati
- Kondisi penyakit turunan yang langka seperti hemokromatosis (dimana tubuh menyerap terlalu banyak zat besi dari makanan yang dikonsumsi)
- Penderita thalesemia yang rutin melakukan transfusi darah
- Anemia hemolitik
- Malnutrisi
Normal
Hasil pemeriksaan transferin yang normal menunjukan keseimbangan dan kondisi sel darah merah yang berfungsi dengan optimal dan fungsi hati Anda baik. Pertahankan kesehatan Anda dengan mengonsumsi gizi yang seimbang, aktivitas fisik yang cukup, serta pemeriksaan kesehatan yang rutin.
Tinggi
Hasil pemerikaan transferin yang tinggi menandakan tubuh memiliki banyak transferin untuk mengikat zat besi, sehingga menyebabkan banyak transferin bebas beredar di aliran darah. Tingginya transferin menandakan tubuh memiliki kadar zat besi yang rendah.
Beberapa penyebab kadar zat besi rendah diantaranya :
- Anemia
- Kehilangan darah atau perdarahan
- Hamil (terutama pada trimester ke 3)
- Menjalani diet vegan atau vegetarian
Konsultasikan ke Dokter yang Tepat
Hasil pemeriksaan transferin pada orang dewasa dapat dikonsultasikan dengan dokter umum, untuk selanjutnya dilakukan pemeriksaan lanjutan ataupun memulai terapi untuk diagnosis yang sesuai. Anda juga dapat berkonsultasi dengan dokter penyakit dalam atau konsultan hematologi-onkologi untuk berdiskusi mengenai masalah Anda lebih jauh. Pada pasien anak, hasil pemeriksaan selain normal harus dikonsultasikan dengan dokter spesialis anak.
Mau tahu informasi seputar hasil pemeriksaan laboratorium, radiologi, dan lainnya? Cek di sini, ya!
- dr Nadia Opmalina
Transferrin. (2022). Retrieved 17 August 2022, from https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=167&contentid=transferrin
Transferrin and Iron Binding Capacitu (TIBC, UIBC). (2021). Retrieved 17 August 2022, from https://www.testing.com/tests/transferrin-and-iron-binding-capacity-tibc-uibc/
Iron Test. (2022). Retrieved 17 August 2022, from https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/iron-tests/
What is an Iron Blood Test?. (2020). Retrieved 17 August 2022, from https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/iron-blood-test