Other Brands/Names
Sodium bicarbonate, Meylon 84-BP
How It Works
Sodium bicarbonate is a systemic alkalinizing agent. It dissociates into smaller particles to release bicarbonate ions, causing the pH of serum and urine to increase. This shift will make the blood less acidic by neutralizing excess hydrogen ion concentration.
Indications
-
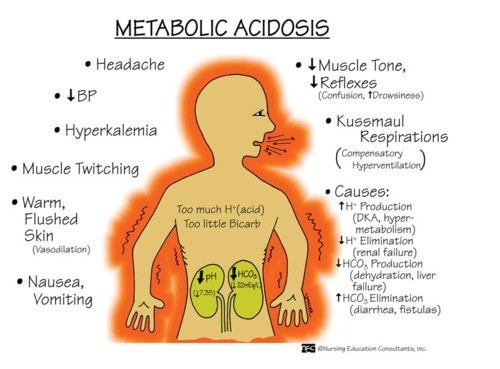
Metabolic acidosis, a state of excessive blood acidity due to various conditions such as severe diarrhea or kidney disease.
-
Dyspepsia, a cluster of upper-abdominal or epigastric discomfort symptoms.
Contraindication
-
Prior hypersensitivity or allergy to sodium bicarbonate.
-
Because it contains sodium, it cannot be given to individuals on a salt-restricted diet.
Side Effects
Nausea, bloating, or belching may occur. If these effects persist or worsen, contact your doctor promptly. Seek urgent medical attention if you develop severe reactions such as chest pain or seizures.
Types
This drug is available in vials, plastic ampoules, and tablets.
Dosage
Metabolic acidosis
To treat metabolic acidosis, the dosage will be adjusted according to the individual's condition, acid-base balance and electrolyte status.
Dyspepsia
1–5 grams every 4–6 hours as needed, or 0.65–2.6 grams every 4 hours.
Safety
Before use, inform your doctor about your complete medical history, especially if you have kidney problems, heart failure, hypocalcemia, or ankle swelling.
During pregnancy, sodium bicarbonate will only be prescribed if indicated. This drug may worsen hypertension in pregnancy. Discuss the risks and benefits of this drug with your doctor if it is needed. This medicine is also excreted in breast milk. Consult your doctor before breastfeeding.
Drug Interactions
Some drugs that may interact with sodium bicarbonate are:
-
Aspirin and other salicylates (e.g., salsalate)
-
Corticosteroids (e.g., prednisone, prednisolone)
-
Memantine
-
Medicines with enteric coatings (stomach-protective coatings)
May reduce the effectiveness of medicines that require gastric acidity, including:
-
Ampicillin antibiotics
-
Atazanavir antivirals
-
Certain azole antifungals (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole)
-
Iron supplements
-
Sucralfate, and others
Consult your doctor or pharmacist for guidance on managing these potential interactions.
Looking for more information about other drugs? Click here!
- dr Hanifa Rahma
BPOM RI. Sodium Bicarbonate. cekbpom.pom.go.id. Retrieved 5 February 2022, from https://cekbpom.pom.go.id//home/produk/69bhknndt7v4km8sdutf8ashf5/all/row/10/page/0/order/4/DESC/search/5/sodium%20bicarbonate
MIMS Indonesia. Sodium Bicarbonate. Mims.com. Retrieved 5 February 2022, from https://www.mims.com/indonesia/drug/info/sodium%20bicarbonate?mtype=generic
Web MD. Sodium Bicarbonate – Uses, Side Effects, and More. Webmd.com. Retrieved 5 February https://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-11325/sodium-bicarbonate-oral/details