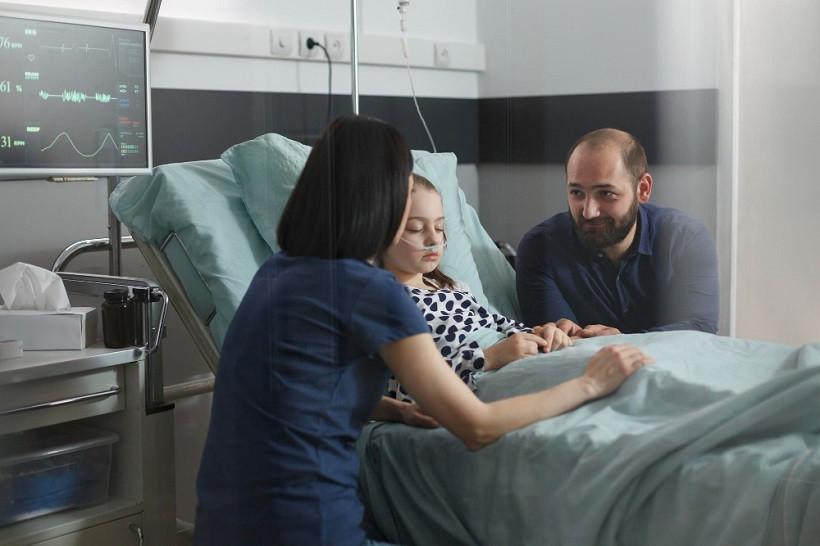
Indonesia has recently experienced a surge in cases of mysterious acute kidney failure affecting children aged 6 months to 18 years. The exact cause of this condition is still under investigation, with the Ministry of Health working closely with various parties to find answers.
In light of the rising number of kidney failure cases, the Ministry of Health has urged the public, particularly parents, to stay calm and vigilant. The Ministry is also working to provide Fomepizole as a free treatment for patients diagnosed with Atypical Acute Progressive Kidney Failure.
Acute Kidney Failure in Children and Its Causes
Acute kidney failure is a rapid and sudden decline in the kidney's ability to filter waste from the blood. It is typically marked by an increase in blood creatinine levels, elevated blood urea nitrogen concentrations, and/or a noticeable decrease or complete absence of urine production. In some cases, kidney function can recover, depending on the severity of the damage.
Several factors can lead to acute kidney failure, including:
-
Reduced blood flow to the kidneys due to bleeding or shock
-
Blockage in the urinary tract
-
Conditions that reduce oxygen supply to the kidneys
-
Hemolytic uremic syndrome caused by E. coli infection
-
Glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the kidney’s glomeruli)
-
Side effects of certain medications that damage the kidneys
Acute Kidney Failure in Indonesia
While the exact cause of acute kidney failure in children in Indonesia is still unclear, many patients exhibit common symptoms such as:
-
Diarrhea
-
Vomiting
-
A fever lasting for 3-5 days
-
Cough and runny nose
-
Reduced or no urination
Reports from the WHO about cases in Gambia suggest that kidney damage in children with acute kidney failure was linked to chemicals found in medications used at home.
In light of this, the Indonesian Ministry of Health has requested tests on syrup medications suspected of being contaminated with ethylene glycol, a substance that was also identified in the Gambia cases.
Understanding Fomepizole and Its Role in Treating Acute Kidney Failure
The Ministry of Health is currently testing Fomepizole as a treatment for patients suffering from acute kidney failure. Preliminary reports suggest that after taking Fomepizole, patients who had not been urinating were able to do so, and children who were unconscious became alert again. So, what exactly is Fomepizole?
Fomepizole is an antidote primarily used to treat poisoning caused by substances like ethylene glycol (found in antifreeze) or methanol, which can be present in fuel, household chemicals, and automotive products. It is often administered alongside hemodialysis, a process to remove toxins from the body.
Fomepizole works by addressing metabolic imbalances and reducing ethylene glycol levels to below 50 mg/dL.
Side Effects of Fomepizole
Like any medication, Fomepizole may cause side effects. The dosage of Fomepizole is tailored to each patient’s condition, and side effects may include:
-
Red skin rash
-
Heartburn
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Diarrhea
-
Loss of appetite
-
Excessive drowsiness
-
Anxiety
-
Headaches
-
A metallic taste in the mouth
-
A drunken sensation
-
Back pain
-
Sore throat
-
Ringing in the ears
-
Changes in vision, smell, and taste
However, it’s important to note that Fomepizole is administered under medical supervision. Doctors will closely monitor your breathing, blood pressure, oxygen levels, kidney function, and other vital signs during treatment.
The hope is that Fomepizole will save the lives of children suffering from acute kidney failure and help reduce mortality. While investigations into the safety of over-the-counter syrup medications continue, it’s essential to always consult a doctor before giving any medication to a child, especially if they are experiencing symptoms like fever, cough, or runny nose. Do not give any medications to your child without consulting a doctor.
- dr Hanifa Rahma
Everyday Health (2020). Fomepizole (Antizol). Available from: https://www.everydayhealth.com/drugs/fomepizole
Medicine.net (2021). Antizol (fomepizole). Available from: https://www.medicinenet.com/antizol_fomepizole/article.htm
Setkab RI (2022). Penjelasan Menkes tentang Kasus Gangguan Ginjal Akut pada Anak. Available from: https://setkab.go.id/penjelasan-menkes-tentang-kasus-gangguan-ginjal-akut-pada-anak/
dr. Siti Nadia Tarmizi, M.Epid (2022). Obat Ganggguan Ginjal Akan Diberikan Secara Gratis. Available from: https://sehatnegeriku.kemkes.go.id/baca/rilis-media/20221025/3641362/obat-gangguan-ginjal-akan-diberikan-secara-gratis/
UPK Kemkes (2022). Waspadai Gagal Ginjal Akut pada Anak. Available from: https://upk.kemkes.go.id/new/waspadai-gagal-ginjal-akut-pada-anak
Stanford Medicine Children's Health. Kidney Disease in Children. Available from: https://www.stanfordchildrens.org/en/topic/default?id=kidney-disease-in-children-90-P03111